LiquidMotor Class Usage#
Here we explore different features of the LiquidMotor class.
Creating a Liquid Motor#
To define a liquid motor, we will need a few information about our motor:
The thrust source file, which is a file containing the thrust curve of the motor. This file can be a .eng file, a .rse file, or a .csv file. See more details in Thrust Source Details
Tank objects, which will define propellant tanks. See more details in Tank Usage
Position related parameters, such as the position of the center of mass of the dry mass, the position of the center of mass of the grains, and the position of the nozzle. See more details in Motor Coordinate Systems
Let’s first import the necessary modules:
from math import exp
from rocketpy import Fluid, LiquidMotor, CylindricalTank, MassFlowRateBasedTank
Then we must first define the tanks:
See also
# Define fluids
oxidizer_liq = Fluid(name="N2O_l", density=1220)
oxidizer_gas = Fluid(name="N2O_g", density=1.9277)
fuel_liq = Fluid(name="ethanol_l", density=789)
fuel_gas = Fluid(name="ethanol_g", density=1.59)
# Define tanks geometry
tanks_shape = CylindricalTank(radius = 0.1, height = 1.2, spherical_caps = True)
# Define tanks
oxidizer_tank = MassFlowRateBasedTank(
name="oxidizer tank",
geometry=tanks_shape,
flux_time=5,
initial_liquid_mass=32,
initial_gas_mass=0.01,
liquid_mass_flow_rate_in=0,
liquid_mass_flow_rate_out=lambda t: 32 / 3 * exp(-0.25 * t),
gas_mass_flow_rate_in=0,
gas_mass_flow_rate_out=0,
liquid=oxidizer_liq,
gas=oxidizer_gas,
)
fuel_tank = MassFlowRateBasedTank(
name="fuel tank",
geometry=tanks_shape,
flux_time=5,
initial_liquid_mass=21,
initial_gas_mass=0.01,
liquid_mass_flow_rate_in=0,
liquid_mass_flow_rate_out=lambda t: 21 / 3 * exp(-0.25 * t),
gas_mass_flow_rate_in=0,
gas_mass_flow_rate_out=lambda t: 0.01 / 3 * exp(-0.25 * t),
liquid=fuel_liq,
gas=fuel_gas,
)
Warning: Adding spherical caps to the tank will not modify the total height of the tank 1.2 m. Its cylindrical portion height will be reduced to 1.0 m.
Note
Here we define two tanks, one for the oxidizer and one for the fuel. We use the MassFlowRateBasedTank, which means that the mass flow rates of the liquid and gas are defined by the user.
In this case, we are using a lambda functions to define the mass flow rates,
but .csv files can also be used. See more details in
rocketpy.motors.Tank.MassFlowRateBasedTank.__init__
Now we can define our liquid motor and add the tanks. We are using a lambda function as the thrust curve, but keep in mind that you can use different formats here.
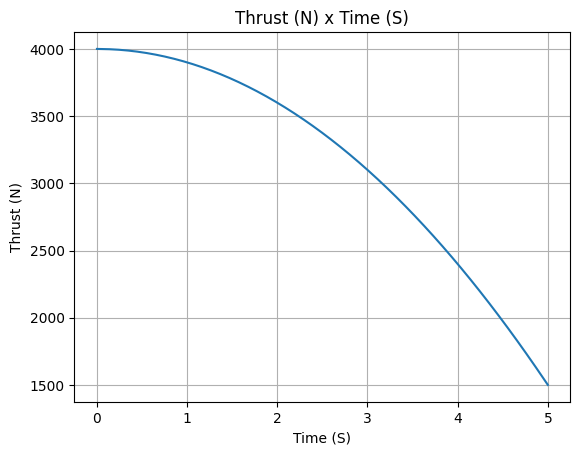
example_liquid = LiquidMotor(
thrust_source=lambda t: 4000 - 100 * t**2,
dry_mass=2,
dry_inertia=(0.125, 0.125, 0.002),
nozzle_radius=0.075,
center_of_dry_mass_position=1.75,
nozzle_position=0,
burn_time=5,
coordinate_system_orientation="nozzle_to_combustion_chamber",
)
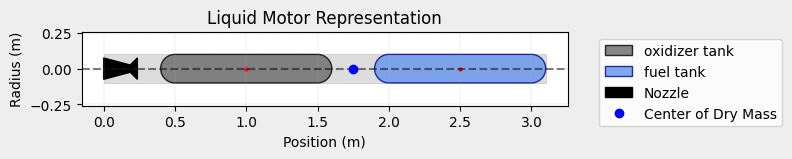
example_liquid.add_tank(tank=oxidizer_tank, position=1.0)
example_liquid.add_tank(tank=fuel_tank, position=2.5)
Caution
Pay special attention to:
dry_inertiais defined as a tuple of the form(I11, I22, I33). WhereI11andI22are the inertia of the dry mass around the perpendicular axes to the motor, andI33is the inertia around the motor center axis.dry inertiais defined in relation to the center of dry mass, and not in relation to the coordinate system origin.center_of_dry_mass_position,nozzle_positionand the tankspositionare defined in relation to the coordinate system origin, which is the nozzle outlet in this case.Both
dry_massandcenter_of_dry_mass_positionmust consider the mass of the tanks.
See also
You can find details on each of the initialization parameters in
rocketpy.LiquidMotor.__init__
And you can find details on adding tanks in Adding Tanks
After defining the motor, we can plot basic attributes using the info()
method.
example_liquid.info()
Nozzle Details
Nozzle Radius: 0.075 m
Motor Details
Total Burning Time: 5 s
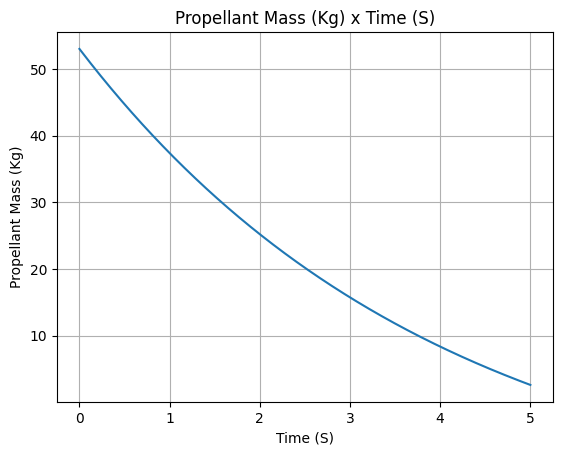
Total Propellant Mass: 53.020 kg
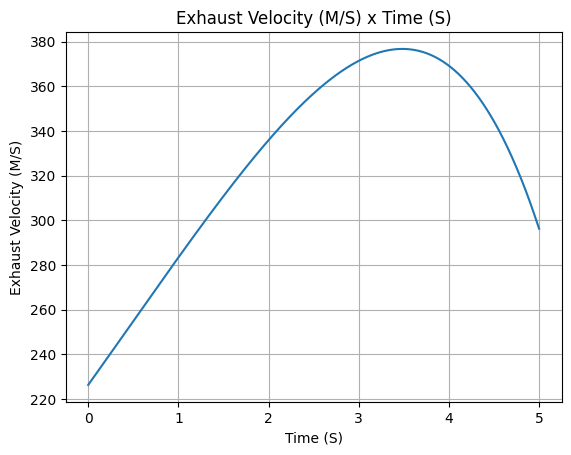
Average Propellant Exhaust Velocity: 327.234 m/s
Average Thrust: 3166.493 N
Maximum Thrust: 4000.0 N at 0.0 s after ignition.
Total Impulse: 15832.466 Ns
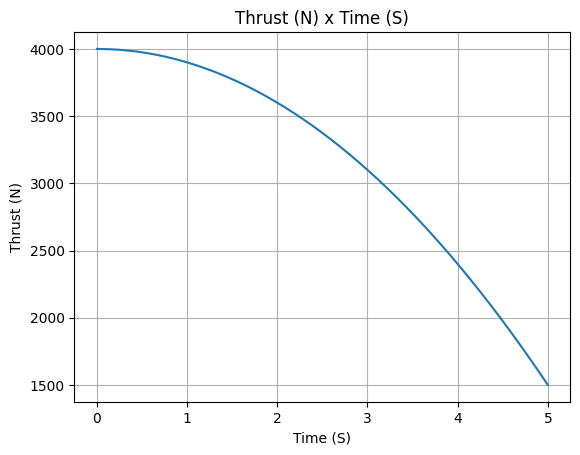
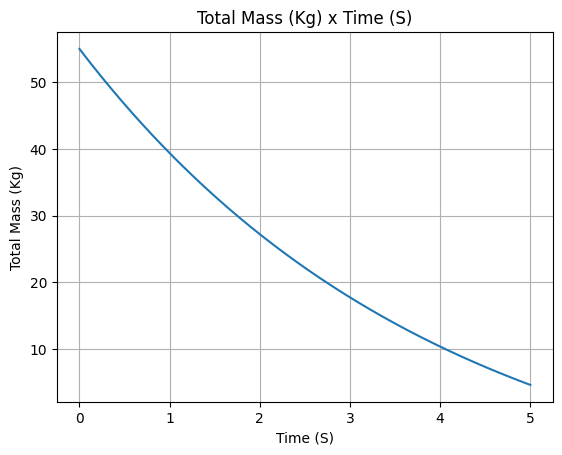
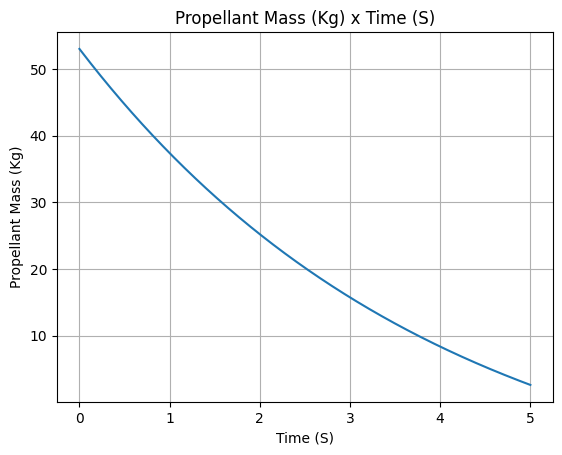
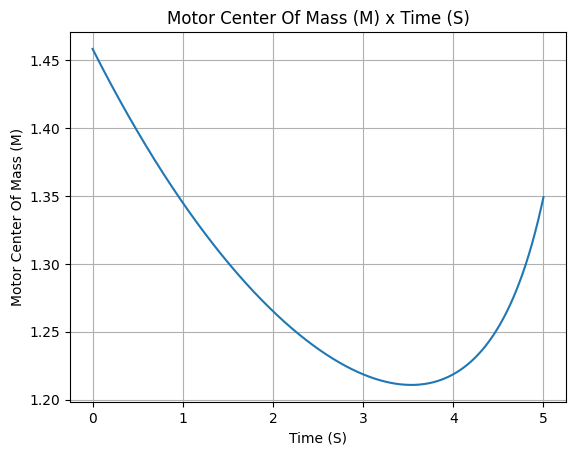
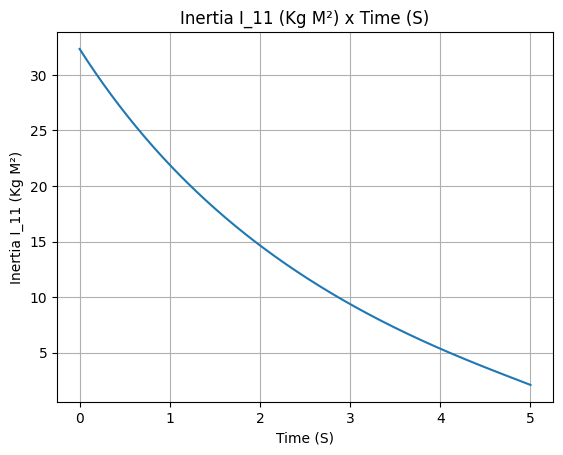
Other plots can also be done, in order to check if the motor is behaving as expected. For example:
Propellant mass
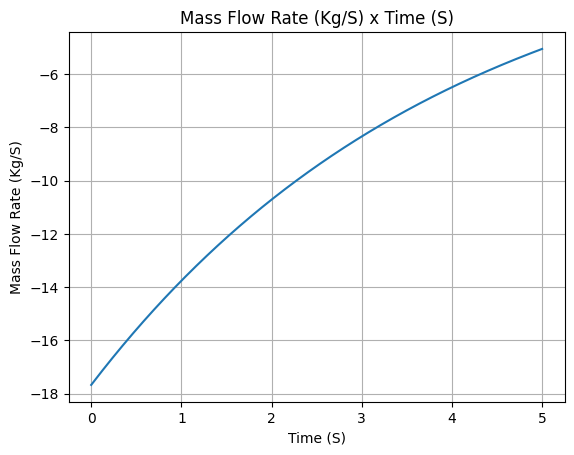
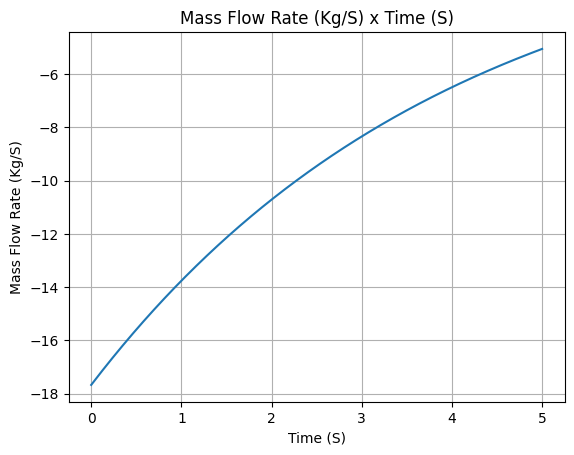
Mass flow rate
Motor center of mass
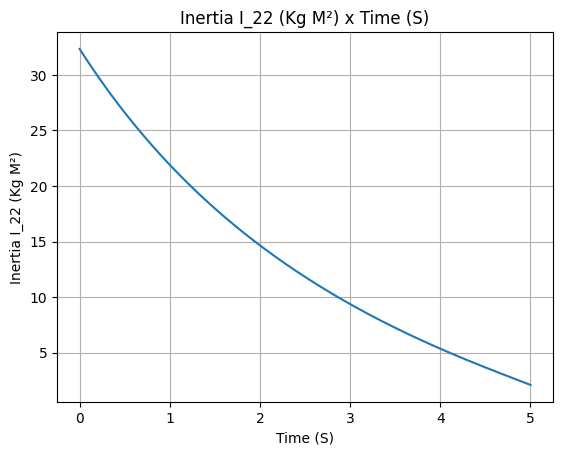
Inertial moment
Exhaust velocity
example_liquid.propellant_mass.plot(0, 5)
example_liquid.mass_flow_rate.plot(0, 5)
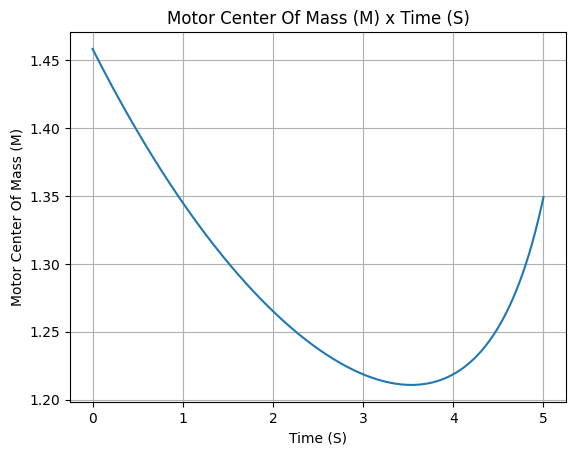
example_liquid.center_of_mass.plot(0, 5)
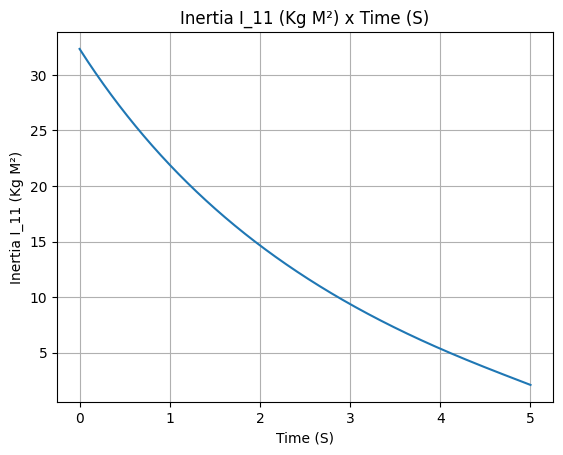
example_liquid.I_11.plot(0, 5)
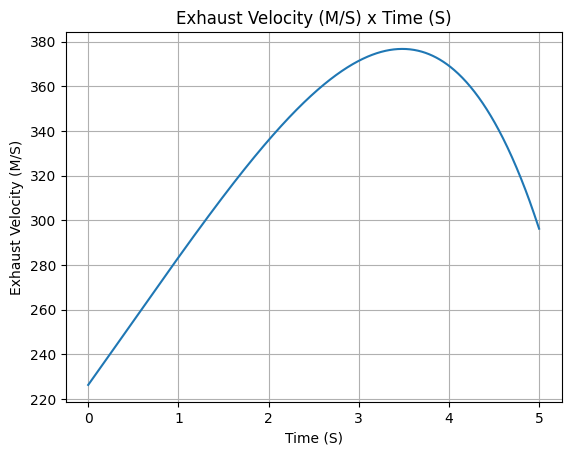
example_liquid.exhaust_velocity.plot(0, 5)
Alternatively, you can plot all the information at once:
example_liquid.all_info()
Nozzle Details
Nozzle Radius: 0.075 m
Motor Details
Total Burning Time: 5 s
Total Propellant Mass: 53.020 kg
Average Propellant Exhaust Velocity: 327.234 m/s
Average Thrust: 3166.493 N
Maximum Thrust: 4000.0 N at 0.0 s after ignition.
Total Impulse: 15832.466 Ns